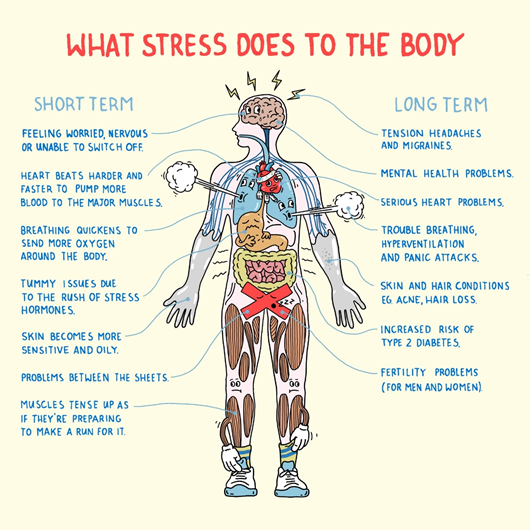
Modern lifestyles require significant amounts of physical and psychological effort to thrive in. A byproduct of this exertion is stress, which affects nervous and endocrine systems significantly.
Stress responses vary per person, and accordingly translate into different physical and psychological effects. Some people are better at coping with and handling stressors than others, but it is certainly possible for everyone to overcome negative effects and thrive.
What are the actual impacts of chronic stress on health?
– Stress produces measurable responses in the neuroendocrine system and behavior. Researchers have been on the quest for the molecular and tissue level alterations that stress causes in hopes of characterizing the effect it has on the human body as a system.
– Chronic stress has been linked to large-scale changes in brain-tissue proportions, with noticeable reductions in size and physical changes in neural tissue. Long-term occupational stress is associated with reduction in size of the hippocampus (Involved in Learning + Memory), caudate + putamen (voluntary skeletal movement), and frontal cortex (personality, concentration, planning).
-Various hormones and peptides released from the body’s stress response initiate complex signaling responses that can compromise the immune, cardiovascular, and muscular systems.
Why should you care?
– Immune Impact: Psychological stress induces the “acute phase response” which also results from tissue damage or infections, to release cytokines and other inflammatory molecules. With chronic stress, the immune system is overstimulated, creating a state of chronic inflammation, leaving the body more susceptible to disease.
– Cardiovascular Impact: Stress causes a release of hormones that affect the stem cells responsible for blood production, causing sustained white blood cell release.
– Muscular Impact: Inflammation associated with chronic stress has been observed to oxidation and degradation of tissue. A key pathway activated by physical exercise has been found to counteract stress-associated depression
What can you do to keep your health A1 and reduce the impacts of stress?
– Maintain proper nutrition and dietary habits
– Get sleep and be mindful
– Exercise!!!
It should be known that there is no way to entirely escape stress (unless you abandon all responsibilities you have and permanently move to an island resort…). All you can really do is try to reduce/manage factors causing stress and take time to protect/heal your body.
Share your comments and questions below. How do you deal with stress?
References:
Blix E, Perski A, Berglund H, Savic I. Long-term occupational stress is associated with regional reductions in brain tissue volumes. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e64065. Published 2013 Jun 11. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064065
Mariotti A. The effects of chronic stress on health: new insights into the molecular mechanisms of brain-body communication. Future Sci OA. 2015;1(3):FSO23. Published 2015 Nov 1. doi:10.4155/fso.15.21
Black PH. Stress and the inflammatory response: a review of neurogenic inflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2002 Dec;16(6):622-53. doi: 10.1016/s0889-1591(02)00021-1. PMID: 12480495.
Agudelo LZ, Femenía T, Orhan F, Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Goiny M, Martinez-Redondo V, Correia JC, Izadi M, Bhat M, Schuppe-Koistinen I, Pettersson AT, Ferreira DMS, Krook A, Barres R, Zierath JR, Erhardt S, Lindskog M, Ruas JL. Skeletal muscle PGC-1α1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell. 2014 Sep 25;159(1):33-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.051. PMID: 25259918.
Savic I. Structural changes of the brain in relation to occupational stress. Cereb Cortex. 2015 Jun;25(6):1554-64. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht348. Epub 2013 Dec 18. PMID: 24352030.
Effects of stress on the body. (n.d.). Retrieved December 26, 2020, from https://au.reachout.com/articles/what-stress-does-to-the-body
How to manage and reduce stress. (2020, August 10). Retrieved December 27, 2020, from https://www.mentalhealth.org.uk/publications/how-manage-and-reduce-stress
[…] A Closer Look at Stress: Impacts on the Human Body […]